|
Page 1 of 3
|
Introduction
Java Servlet is the one of the most important Java
technologies. It is the simplest model to build a complete Java J2EE
Web Application. Furthermore, even for complex J2EE Web Application
that uses Struts, Spring, EJB and etc, they are still using Servlet for
certain purposes such as Servlet Filter, Listener and etc. Thus, it is
just a good idea for you to have well-built understanding of Java
Servlet. Prior reading this tutorial, it would be excellent if you have
mastered the basic Java programming languages.
At the completion of the tutorial, you are expected
to comprehend the concept of the Java Servlet, be familiar with the
ways to create Java Servlet using NetBeans 5.0, differences between
POST and GET and should be ready to go to the next level.
|
|
|
|
In this tutorial, we are going to create one dynamic web application
that asks the user for first name and surname. Then the system should
response by greeting the users.
The tutorial consists of four main steps.
- Introduction to NetBeans 5.0
- Creating New Web Application Project in NetBeans 5.0
- Implementation of Tutorial’s Example
- Conclusion
Introduction to NetBeans 5.0
Nowadays, NetBeans is one of the most powerful Java programming IDE.
Other popular Java IDEs are also available in the market such as
Eclipse, Bea WebLogic Workshop, IBM WebSphere Application Development
(WSAD) and etc. Creating and implementing Java Servlet using NetBeans
is extremely straightforward and simple. This is one of the reasons why
NetBeans rapidly grow its popularity. Additionally, it has Tomcat
bundled together within the NetBeans hence compiling and deploying Java
Servlet is just a few clicks on your mouse. Well, without going any
further, let’s start our tutorial.
Creating New Web Application Project in NetBeans 5.0
Creating a Java Servlet means that you are required to deal with JSP
(JavaServer Pages). JSP is actually a HTML but unlike HTML, JSP may
have Java codes (usually we call it as Scriptlet) embedded in it. In
short words, we may represent JSP as dynamic HTML. In Java J2EE Web
Application, JSP plays as a front-end while Java Servlet is the
controller that contains the business logics, complex algorithms and
etc.
For example, consider “Online University Student Registration
System” developed in Java J2EE Web Application, the registration page
where you fill in your details such as your name, your address, your
username and etc are actually a JSP page. Later on, when you have
completed filling out all the details and you press the submit button,
all the information will be sent to Java Servlet for further processes.
Java Servlet receives this information, does the necessary processes
such as validations, generating user id and etc and then keeps the
information to database. After successfully saving the data to
database, Java Servlet redirects the user to the success page where the
user can log in to the system. Likewise, if there is an unexpected
error occurred happening in the middle of student registration system’s
process, the user will be redirected to the error page.
Okay, without any more delay, let’s get ready for our tutorial.
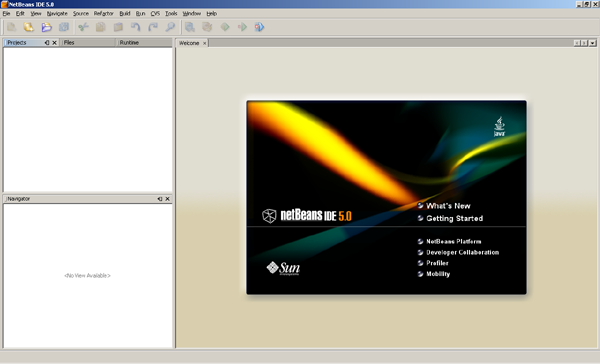
Start your NetBeans 5.0. After it has been completely started, it
should look like below screenshots.

First, we have to create a new Web Application Project for our Java
Servlet. This Web Application contains all the JSP pages as well as our
Servlet classes. To create a new Web Application in NetBeans 5.0, you
can go to the menu and choose File > New Project. A wizard will
instantly be displayed to you and you are required to provide some
information to configure your Web Application.
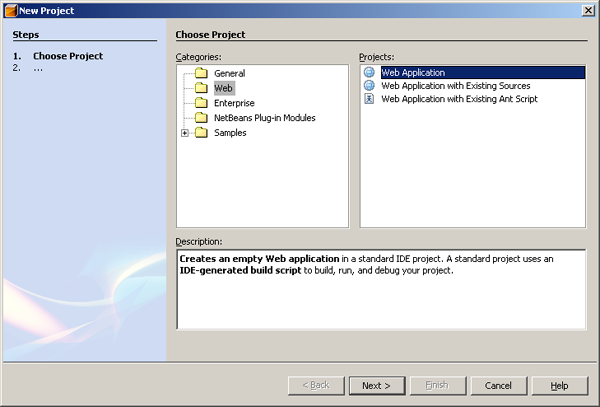
As the wizard is displayed as shown on above illustration, choose
Web on the left panel and Web Application on the right panel and click
Next button. All the other options are used to develop other kind of
projects in NetBeans and irrelevant for our tutorial.
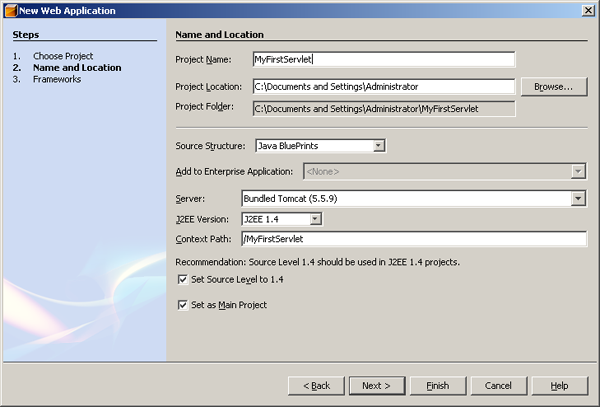
In the next step or the second step of configuring our Web
Application, you can provide your Web Application a name. Well, please
feel free to name it whatever you want. In this case, to make it
self-explanatory, I name our Web Application as MyFirstServlet as shown
in the above illustration. In the middle of the wizard, there is an
option called Server and it has the value of Bundled (Tomcat 5.5.7). It
demonstrates that NetBeans 5.0 will use its bundled Tomcat as the
default server. Other configuration should remain the same and press
Finish button. You can also press the Next button to go to the last
page where you can define the frameworks that you would like to use as
shown in below illustration. However, we can skip the last step as we
do not use any framework for our Java Servlet. Okay, we have completed
our configuration of Web Application and we are ready to implement our
first Java Servlet. Grab your coffee and we are ready to go.
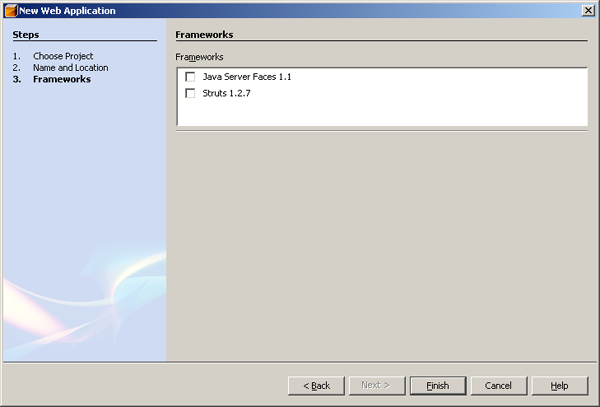
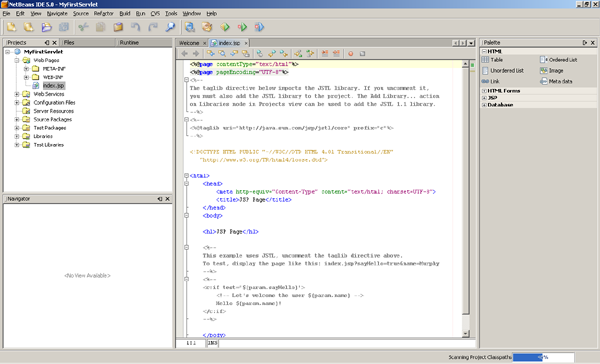
After completing the Web Application’s configuration, you should
have a screen similar as below. It will also create one default JSP
file called index.jsp on your Web Pages folder.
<< Start < Prev 1 2 3 Next > End >>
|



Excellent topic included with Netbean 5.0 editor